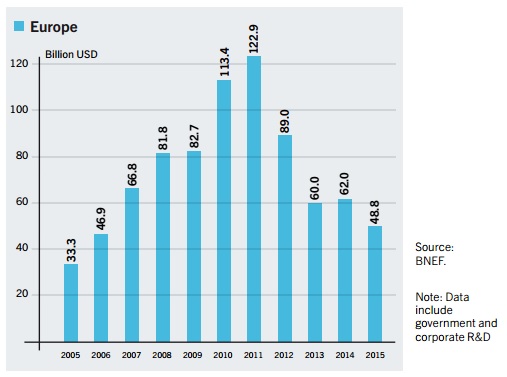
Europe is losing its status as a renewable energy leader as investment in clean energy plummeted 21 percent in the region last year to $48.8 billion – the lowest total since 2006.
Globally, investment in renewable energy soared to a record $328.9bn in 2015, according to a new study released by REN21, an international coalition of governments, renewable energy trade associations, and financial institutions including the International Energy Agency and the World Bank.
Overall, however, investment in developed countries declined 8 percent last year to $130bn, with Europe seeing the most significant decrease as investment dropped $13.2bn between 2014 and 2015.
This is despite Europe’s record year of financing offshore wind power to the tune of $17bn, up 11 percent from the year before.
As the report shows, the pace of investment in renewable energy in Europe has been slowing down since 2011, dropping some $74bn over four years.
This comes after a steady increase seen between 2005 and 2011 from $33.3bn to $122.9bn.
The report attributes Europe’s steep drop in investment last year to a sluggish economy and policy changes to subsidies.
Investment in China, US, and Emerging Markets
Meanwhile the U.S. and China continue to surge ahead with investment up 19 percent and 17 percent respectively.
And for the first time in history, 2015 saw the total investment in renewable power and fuels in developing countries exceed that in developed economies.
Christine Lins, Executive Secretary of REN21, said: “What is truly remarkable about these results is that they were achieved at a time when fossil fuel prices were at historic lows, and renewables remained at a significant disadvantage in terms of government subsidies.”
But out of the seven forms of renewable energy technology analysed in the report, solar and wind power were the only two to see an increase in new investment in 2015. Solar investment rose 12 percent, followed by a 4 percent increase in wind power investment.
Arthouros Zervos, Chair of REN21, said: “The renewables train is barrelling down the tracks, but it’s running on 20th century infrastructure – a system based on out-dated thinking where conventional baseload is generated by fossil fuels and nuclear power.
“To accelerate the transition to a healthier, more-secure and climate-safe future, we need to build the equivalent of a high-speed rail network – a smarter, more flexible system that maximises the use of variable sources of renewable energy, and accommodates decentralised and community-based generation.”
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts