The Oregon legislature just put another nail in the coffin of the coal era.
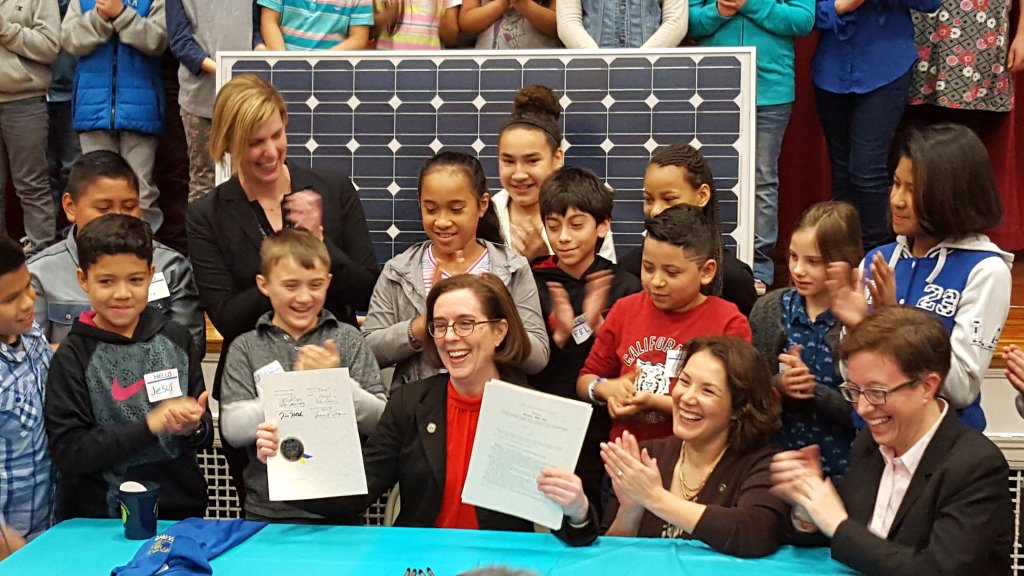
On Friday, Oregon governor Kate Brown signed into law one of the most ambitious and sweeping pieces of energy legislation in the country’s history, one which will eradicate the use of coal for electricity generation entirely within two decades.
The pioneering law makes Oregon the first state in the nation to legislate a ban on coal for the electric supply, while also mandating that utilities provide half of their electricity from new renewable sources by 2040.
Add those new renewables to Oregon’s existing hydropower resources and, in less than 25 years, the state’s electric sector will be between 70 and 90-percent carbon-free, one of the cleanest energy portfolios in the country.
Currently, coal supplies roughly 30-percent of the state’s electricity.
“Knowing how important it is to Oregonians to act on climate change, a wide range of stakeholders came to the table around Oregonians’ investments in coal and renewable energy,” said Governor Kate Brown. “Working together, they found a path to best equip our state with the energy resource mix of the future. Now, Oregon will be less reliant on fossil fuels and shift our focus to clean energy. I’m proud to sign a bill that moves Oregon forward, together with the shared values of current and future generations.”
Oregon Governor Kate Brown, surrounded by those who will benefit the most, signs the Clean Energy and Coal Transition Plan into law. Photo Credit: RenewOR
In Blue Oregon, Nick Abraham of Oil Check Northwest described this remarkable coalition of groups that came together to push for the law, an alliance that included ratepayer advocates, green groups, and the utilities themselves.
“CUB believes that this a big victory for utility customers. Coal is a huge financial risk and we are mitigating this risk by moving away from coal and investing in clean energy instead,” said Bob Jenks, Executive Director of the Citizens’ Utility Board of Oregon, the ratepayer advocacy group.
Still, the legislation was fought tooth and nail by clean energy opponents in the state senate, particularly Republican Ted Ferrioli (who, according to Abraham, “takes tens of thousand from oil, gas and coal companies” every year). But, again, the utilities impacted by the law support the measure.
“Our company has been reducing reliance on coal generation and expanding our renewable energy portfolio for the past 10 years as market forces, regulation and evolving customer preference continue to drive change in the way electricity is generated and delivered,” stated Stefan Bird, President and CEO of Pacific Power. “This landmark legislation allows us to effectively manage Oregon’s transition to a clean energy future in a manner that protects customers from cost impacts, ensures grid reliability and allows us to meet all of our responsibilities to the communities we serve.”
This sentiment was echoed by Jim Piro, president and CEO of Portland General Electric, the state’s largest electric utility.
“The path forward was forged through a collaborative process where we all tried to balance stakeholder needs,” said Piro in a statement. “We look forward to working with the Public Utility Commission and all of our stakeholders to implement this policy in a way that benefits the environment, manages price impacts for our customers, and ensures that the reliability of the electric grid is not compromised.”
Clean energy advocates who fought for passage of the bill are celebrating. “Oregon had a clear choice to make: do we want to power our homes with coal or with clean energy? Today it is clear we chose clean,” said Oregon Environmental Council Executive Director Andrea Durbin in a press release. “Kissing coal goodbye and doubling renewable energy will give Oregon some of the cleanest power in the country, delivers clean energy for all Oregon families and re-establishes our state as a leader in green.”
It will also effectively clean up the grid in neighboring states. Because of how the utilities procure their power, the impacts of the law will be felt throughout the whole northwest, as Noah Long and Angus Duncan explain on NRDC‘s Switchboard:
Although one-third of Oregon’s electricity today comes from coal-fired plants, the only in-state facility was already slated to retire by 2020. However, the two affected utilities supply power to Oregon from coal facilities they own in Utah, Wyoming, and Montana. By ending Oregon’s investments, the market for dirty energy will shrink – which should speed the retirement of those aging plants.
At the same time, the law doubles the amount of energy from new renewable resources that Pacific Power and Portland General Electric must provide to their Oregon customers. Therefore, the utilities will be obliged to look first to wind, solar and other clean energy sources – and not new base-load natural gas turbines – to replace those aged coal plants.
Many state and national clean energy advocates have upheld the Clean Electricity and Coal Transition Plan as a precedent setting model for other states to follow.
“This landmark climate legislation puts Oregon on a bold new course,” said Kristen Sheeran, Oregon Director of Climate Solutions. “Moving away from coal and oil toward clean, renewable electricity raises the bar for clean energy in other states.”
Indeed, no other state has yet legislated an end to coal-powered electricity. (Though Hawaii and Vermont do boast electric grids that already operate free of coal.)
The renewable energy standards that the transition plan mandates put Oregon amongst the small handful of states that have renewable standards of 50-percent of more. Hawaii, again a leader, will require a full 100-percent by 2045; California and New York now both require 50-percent within 25 years; Massachusetts is demanding a 1-percent annual increase indefinitely, until it reaches the full electric portfolio.
Now, given the state’s mandate to scrap coal from its electric mix, if the “thin green line” of Cascadia activists can continue to block coal exports from the state’s ports, Oregon can effectively bid adieu to coal entirely.
Blog image: Boardman Oregon coal plant (Wikimedia Commons)
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts