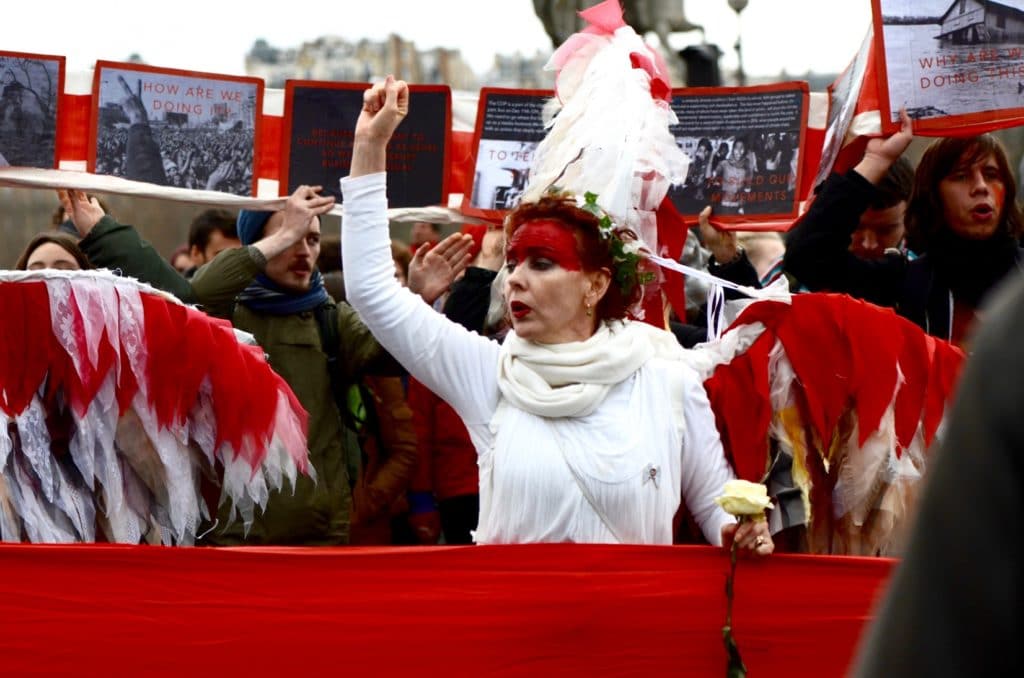
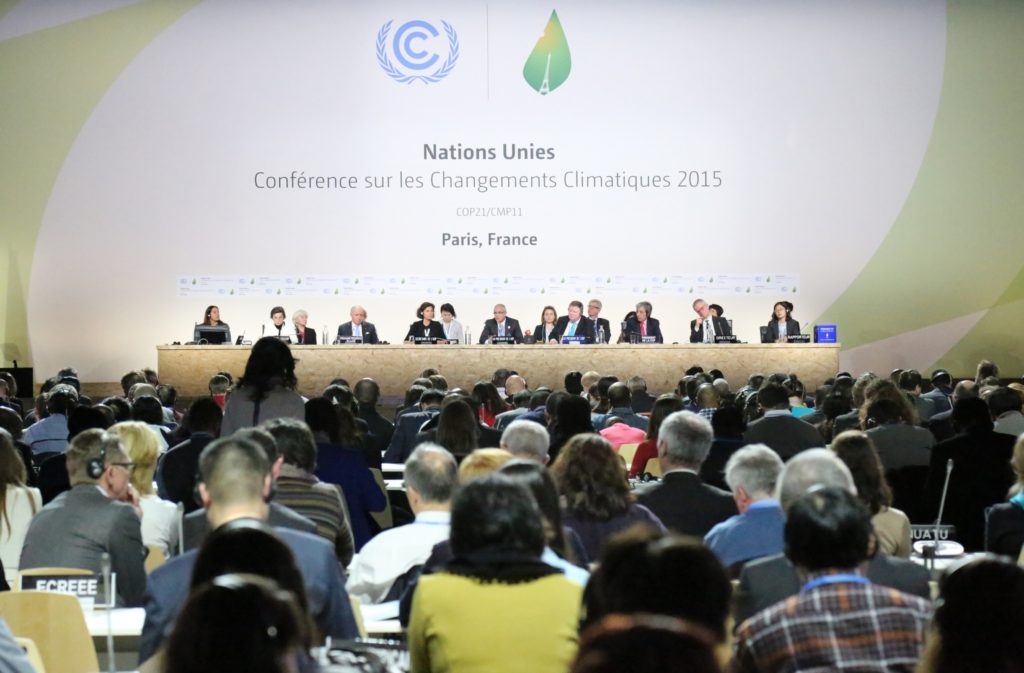
The 21st session of the Conference of the Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) took place in December 2015, in Paris, France. Governments representing more than 190 nations agreed an historic new global Paris Agreement on climate change. The aim is to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions to avoid dangerous climate change.
Scientists have warned that if greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, we will pass the threshold of 2C global warming above pre-industrial temperatures; beyond this climate change becomes catastrophic and irreversible. Current climate commitments expire in 2020, so governments must now produce an agreement on what happens after that.
Carbon dioxide is one of the main drivers of climate change and burning fossil fuels is a primary source of this greenhouse gas. To tackle climate change we must therefore significantly reduce our reliance on coal, oil and gas – an unwelcome idea for big energy companies whose profits rely on these assets. This DeSmog UK series showcases our coverage from inside the COP21 conference. It also investigates the fossil fuel industry’s actions in the lead up to and during the Paris climate conference.